10 things to know about sleep as the clocks go back
9. Are other countries doing it differently?
One study looked at sleep habits in 20 industrialised countries.
It found variations of up to an hour in the time people went to bed and woke up, but overall sleep duration was fairly constant across countries. Generally, if a population on average went to bed later, they woke up later too, although not in every case.
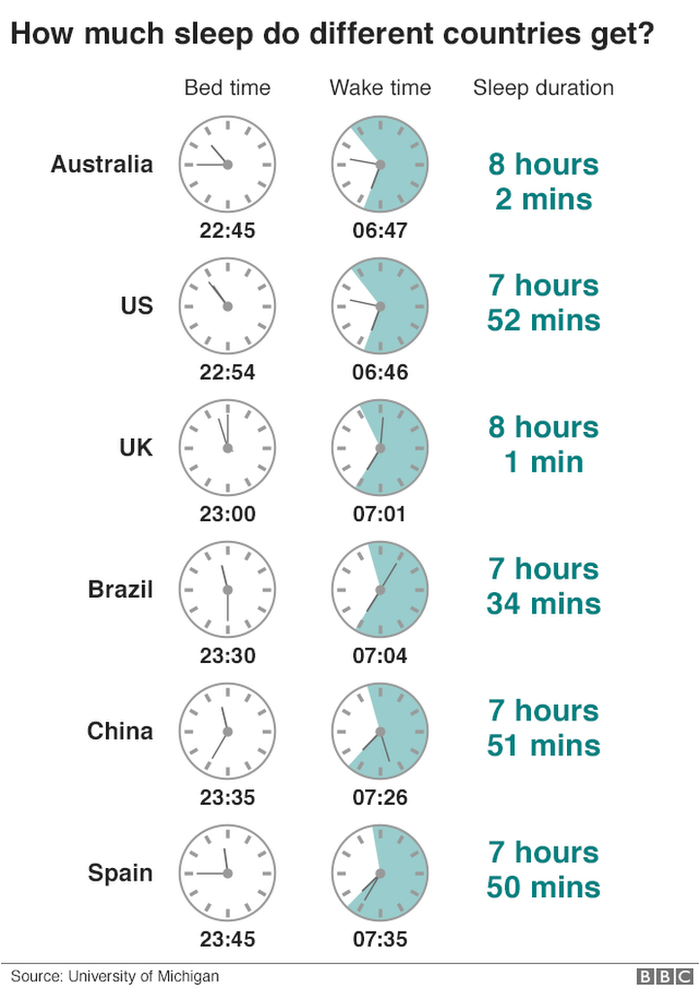


Researchers have concluded that social influences - hours worked, timing of school, leisure habits - play a far bigger role than the natural cycle of light and dark.
In Norway, where the period of lightness each day varies through the year from zero to 24 hours, sleep duration throughout the year only varies on average by about half an hour.
Both in countries like the UK, where dusk and dawn times vary considerably across the seasons, and in countries closer to the Equator where dusk and dawn times vary minimally, sleep duration remains constant through the year.
But what about the impact of artificial light?
A study of three communities who had no access to electricity, in Tanzania, Namibia and Bolivia, found the average sleep duration was 7.7 hours - in step with industrialised countries.
So sleep duration seems remarkably consistent throughout the world - it's the time we all go to bed and wake up that varies slightly.
These pre-industrialised communities did not fall asleep as soon as it got dark, but around three hours after sunset and generally woke before sunrise.
Most studies in this area suggest that artificial light delays sleep time but does not necessarily decrease overall sleep duration.
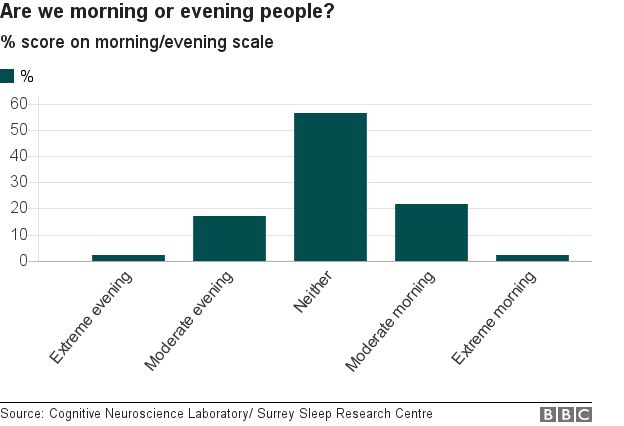
10. Morning larks, night owls?
There have always been morning people and evening people. We even have genetic evidence that backs this up.
But the introduction of artificial light appears to have exacerbated this effect, particularly for people who prefer to stay up late.
If you are already inclined towards being a night owl, artificial light will make you stay up even later.
About 30% of us tend towards being morning people and 30% towards being evening people, with the other 40% of us somewhere in the middle - although marginally more people prefer early rising to late nights.
We do have some control over our body clocks, however. Those who are naturally late to bed and late to rise can try reducing their exposure to light in the evenings and making sure they get more light exposure in the daytime.
A team of researchers took a group of volunteers camping in Colorado, where they had no access to artificial light. Only 48 hours was enough to shift the campers' body clocks forward by almost two hours.
Levels of melatonin, the hormone that tells our body to prepare for sleep, began rising earlier in the volunteers - their bodies were preparing for sleep much closer to sunset.
Share This Post